Tumors of the third ventricle of the brain
3 November 2023

3 November 2023


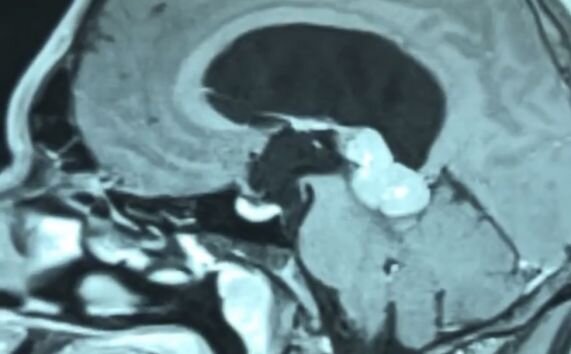
Tumors of the third ventricle of the brain are represented by neoplasms of various histological variants: astrocytomas, craniopharyngiomas, colloid cysts, gliomas of the chiasm (crossing of the optic nerves) with growth into the third ventricle, adenomas of the pituitary gland, pineocytomas, pineoblastomas (tumors of the pineal gland), gliomas, gangliocytomas, tumors from embryonic cells (germinomas, embryonal carcinomas, choriocarcinomas, teratomas, suprasellar tumors), as well as glial cysts, etc.
In the neurosurgical classification, depending on the location of the tumor, three groups are distinguished:
Tumors of the third ventricle are rare and account for 5 to 8% of cases, and are more common in young people.
Clinical symptoms of tumors of the third ventricle of the brain correspond to typical signs of intracerebral tumors: headache, nausea, vomiting, lack of effect from taking painkillers, impaired balance, coordination of movements. Tumors of the third ventricle often cause depression of consciousness, drowsiness. With progressive growth, it is characterized by sudden attacks of headache with vomiting, noise in the ears, visual disturbances (flickering flashes of light, "flies" in front of the eyes, feeling of "shadows" in the eyes).
Diagnosis involves CT and/or MRI of the brain with contrast.
Tumors of the third ventricle of the brain require a complex approach, which includes all types of therapy - surgical removal, radiation therapy, chemotherapy treatment. Depending on the histological and pathomorphological characteristics of the neoplasm, the treatment scheme is selected in accordance with the diagnosis and clinical situation, but surgical removal in most cases is the first stage of treatment, followed by radiation and chemotherapy. But the key goal of neurosurgical intervention is the elimination of hydrocephalus of the lateral ventricles, which is observed as a result of obturation of the third ventricle by a tumor. Elimination of hydrocephalus makes it possible to perform direct surgical intervention to remove the tumor. In the case when it is technically impossible to carry out endoscopic perforation of the bottom of the third ventricle, CSF-peritoneal shunting is performed.
Taking into account the deep location of tumors, preference is given to the standards of Europe and the USA, which provide for the use of minimally invasive, highly accurate and highly effective microsurgical techniques, which were introduced in the "Oberig" clinic by the leading Ukrainian neurosurgeon, Doctor of Medicine, Honored Doctor of Ukraine, Professor Andriy Oleksandrovich Danchyn
In the "Oberig" clinic, patients with the most complex neurosurgical pathology can receive specialized care at the level of the best global standards.
Call: 044 521 30 03 or sign up for a consultation on the website: https://my.oberig.ua/ua/appointment/
