Aneurysms of cerebral arteries
4 October 2023


4 October 2023


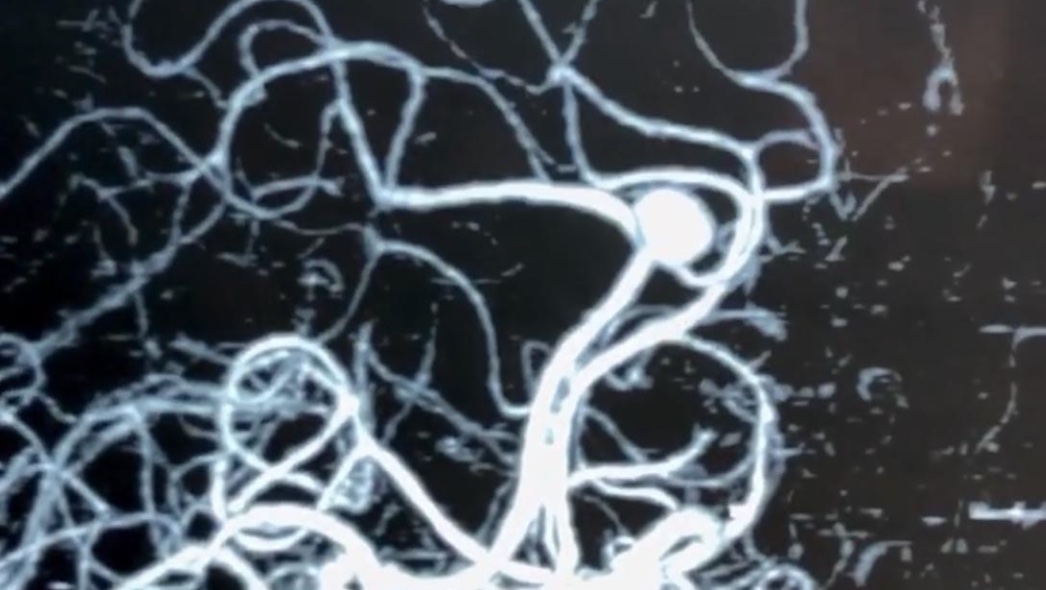
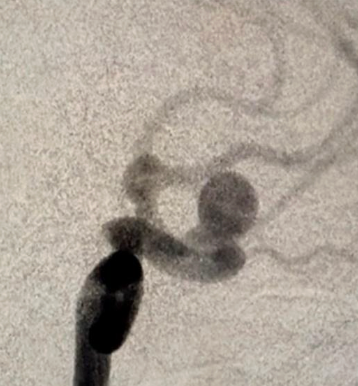
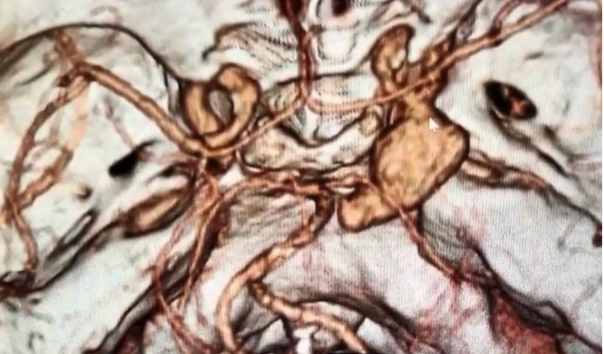
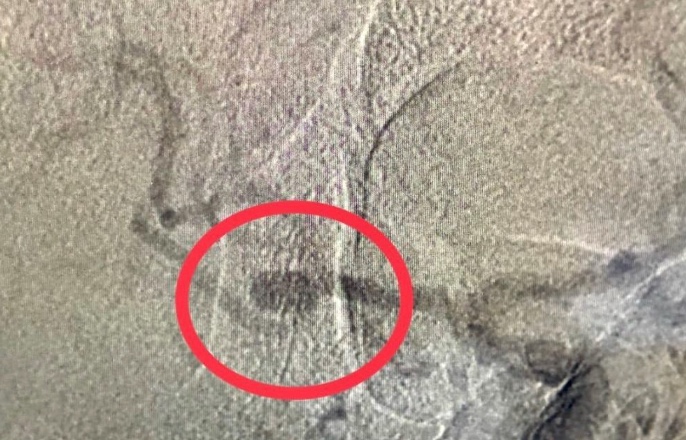
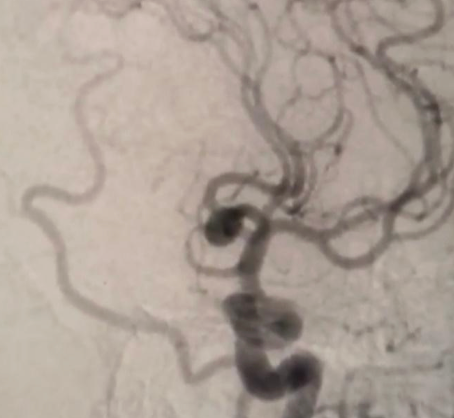
Aneurysms of cerebral arteries are vascular pathologies in which the wall of an artery bulges. According to the shape of the protrusion, saccular and spindle-shaped (fusiform) aneurysms are distinguished. The cause of aneurysms is not known for sure. Among the etiological factors can be congenital predisposition (defects of the muscle layer of the wall of cerebral vessels); atherosclerotic (combined with congenital defects of the wall of cerebral vessels); embolic, infectious, traumatic factors.
According to the location of saccular aneurysms, the most common are:
Asymptomatic, uncomplicated aneurysms may be an incidental finding during head examinations for other diseases. Clinically, aneurysms are manifested in the event of the development of complications — a sudden rupture with hemorrhage into the brain or subarachnoid space. Sudden ruptures of aneurysms are characteristic of young people. In 30% of all cases, subarachnoid hemorrhages occur during sleep.
Brain MRI, cerebral angiography, CT angiography.
If uncomplicated aneurysms are detected, planned neurosurgical intervention is carried out using the methods of aneurysm clipping or balloon angioplasty (endovascular closure of the protrusion of the vessel wall).
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the general condition of the patient, anatomical features and location of the aneurysm, the moment of detection in relation to the development of complications (before rupture or after rupture).