Hydrocephalus
11 October 2023
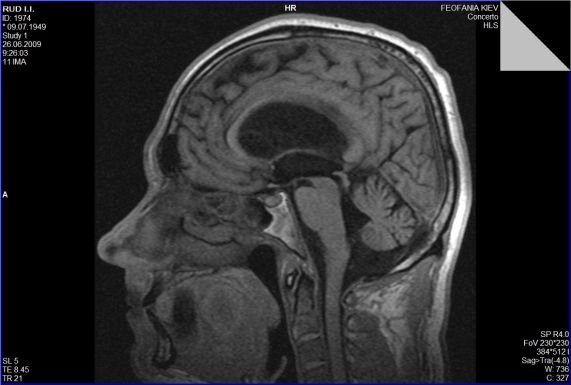

11 October 2023


Hydrocephalus, or hydrocephalus, is a pathological condition characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles of the brain and intermembrane spaces.
According to the pathogenesis of hydrocephalus, two types are distinguished: occlusive hydrocephalus (when there is an obstacle to the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the circulatory system of the brain from the place of its secretion in the ventricles to the place of its absorption - in the subarachnoid systems/subarachnoid space) and aresorb).
The causes of hydrocephalus are diverse: congenital malformations of the brain (Chiara malformations of the 1st and 2nd types, myelomeningocele, primary stenosis of the aqueduct of the brain, Dandy-Walker malformation (atresia of the foramina of Lushka and Majanda); acquired hydrocephalus of infectious parasitic diseases (for example, cysticercosis ), hydrocephalus due to hemorrhage in the brain (insulitis, ruptured aneurysms, intraventricular hemorrhages, etc.), with non-tumor and tumor diseases of the brain, neurosarcoidosis, hydrocephalus associated with spinal tumors.
Hydrocephalus can be suspected on the basis of complaints of headaches, dizziness, nausea, impaired vision, impaired coordination of limb movement, decreased memory, attention and other cognitive abilities, impaired pelvic organ function (urinary incontinence).
For the purpose of examination and verification of the diagnosis of hydrocephalus with subsequent neurosurgical intervention, it is possible to contact the Center of Neurosurgery "Obereg". The list of examined includes a standard laboratory package of general clinical tests and MRI of the brain.
The main method of neurosurgical treatment is the shunting of brain ventricles, however, in the Center of Neurosurgery, the author's technique of the head of the Center, Andrey Danchin, is implemented, which provides for microsurgical endoscopic intervention with the formation of holes in the walls of the ventricles for unobstructed circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which has been successfully used for more than ten years. replacement of shunts
