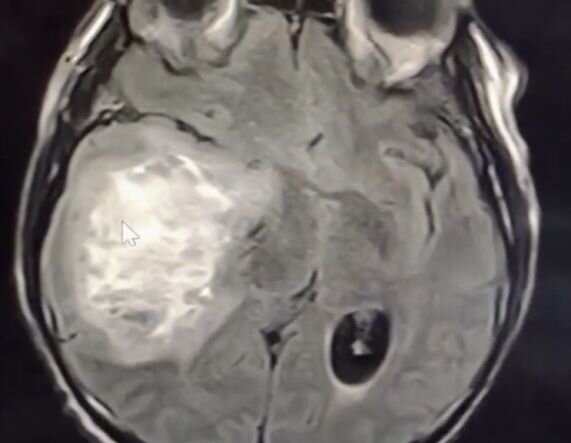
Astrocytomas of 1 — 4 degrees of malignancy
Astrocytoma belongs to the group of tumor diseases (gliomas) of the central nervous system. Depending on the degree of malignancy, astrocytomas are classified into 4 types:
- Pilocytic astrocytoma. It refers to gliomas of a low degree of malignancy (grade 1) and is characterized by a good survival prognosis, especially at a young age. More often, pilocytic astrocytomas occur in young people and adolescents and tend to be located in the temporal lobe of the hemispheres, the hypothalamus, the cerebellum, the posterior frontal and anterior parietal areas, the region of the junction of the optic nerves, and the brain stem. Juvenile pilocytic astrocytomas, unlike fibrillary astrocytomas, rarely become malignant. Slow growth and cystic nature without infiltration of neighboring brain tissues are characteristic of pilocytic astrocytes. Despite the relatively benign nature of pilocytic astrocytoma, the ultimate nature of this tumor is not benign, so early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prognosis. A worse prognosis in pilocytic astrocytoma is observed in the course of the disease with increased intracranial pressure, impaired consciousness, personality changes, gross neurological deficit, a short period of diagnosis from the moment of symptoms, contrast enhancement during neuroimaging.
- Fibrillary astrocytoma. This type of astrocytoma predominates among all other types of brain tumors. Compared with pilocytic astrocytoma, fibrillary astrocytoma has a higher degree of malignancy (grade 2). The speed of its malignancy is six times* compared to pilocytic astrocytoma (*when detected in patients older than 45 years compared to young patients). Unlike pilocytic astrocytoma, fibrillary astrocytoma usually does not have clear boundaries, is characterized by diffuse penetration into brain tissue, and is difficult for surgical removal.A characteristic feature of astrocytoma of a low level of malignancy (grade 1-2) is the presence of seizures. Features of CT and MRI images of astrocytes of various degrees of malignancy can be found in the material here - https://oberig.ua/en/news/statti/osoblivosti-kt-ta-mrt-kartini-pri-astrocitomax-877
- Anaplastic astrocytoma (grade 3). It occurs more often after the age of 30 (average age - 46 years), the male gender prevails among patients. It is usually located in the hemispheres of the brain, is distinguished by a rapid increase in size and infiltrative growth in the adjacent brain tissue without clear boundaries.
- Glioblastoma multiforme. This is the most dangerous and malignant type of brain glioma - grade 4. It is characterized by rapid growth, sprouting to other brain structures (cerebellum, thalamus, hemispheres). Affects older men more often (average age - 56 years).
Malignant astrocytomas (anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma multiforme) can arise as a result of malignancy by low-grade astrocytomas (pilocytic and fibrillary astrocytomas), but more often arise as a primary neoplasm.
Forecast
The prognosis is influenced by several factors, among which age can be distinguished into two groups of factors:
The first group of factors is directly related to the parameters of the tumor: the localization of the tumor process, the presence of sprouting into neighboring and other brain structures, the spread to functional and vital parts of the brain, the histomorphological nature of the tumor, the presence/absence of gene mutations, the possibility of surgical removal, the sensitivity of tumor cells to antiblastic drugs and the effect of radiation therapy.
The second group of factors is related to the patient's condition: age, presence of concomitant and transferred diseases, general condition, severity/severity of the symptoms of the main disease (neurological deficit, cognitive impairment, etc.) and psycho-emotional mood of the patient. It is worth noting that most intracerebral tumors have a recurrent nature, which is observed even under the conditions of combined therapy. Factors that contribute to prolonging the recurrence-free period and increasing the overall life expectancy are a low degree of tumor anaplasia, the radicality of tumor resection, the young age of patients (up to 45 years), and the absence of neurological disorders in the postoperative period.
Diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors using world-class technologies is possible at the Neurosurgery Center of the Universal Clinic "Oberig", which is headed by Andrii Oleksandrovich Danchyn - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Honored Doctor of Ukraine, neurosurgeon with 26 years of experience. His experience and expertise have saved thousands of lives for patients with neuro-oncology diagnoses.
Call: 044 521 30 03 or sign up for a consultation on the website: https://my.oberig.ua/ua/appointment/